The DRS learning algorithm is an extension of the Random Optimisation Method, and tends to perform random steps in the analysis space. For a compact set, the Random Optimisation Method guarantees convergence at the local minimum.
Improvements were made for the DRS such as the possibility of performing reverse steps and self-correcting variance, as well as the addition of a direct component that introduces a certain amount of inertia in the motion.
Given the complexity of the correlations to be learned and the large variability of the possible conditions, a network was selected with two intermediate layers that guarantees enhanced generalisation capacity.
This full connected, feed-forward network has 20 neurons in the first hidden layer and 18 in the second.
The following parameters were used as network input for each quality (for a total of 4 types of quality):
Quantities available in the yard
Time/quantity index of the next arrivals of materials
Amount of the next arrivals of materials
Time/quantity index of the next deliveries
Amount of the next deliveries
Proximity of ocean-going ships with that type of coal not yet booked
These 16 neurons are matched with another 8 corresponding to the following variables:
Occupation level of the loading dock
Occupation level of the unloading dock
Operating efficiency of the unloading line
Operating efficiency of the loading line
Operating efficiency of the Transhipment line
Desired cost level
Compliance level relative to material delivery terms
The following terms were used for output variables for each type of coal:
Y1 Opportunity to call a new ocean-going ship (yard load)
Y2 Opportunity of increasing the transhipment quantity
Y3 Opportunity of calling a new small coasting ship (yard unloading)
Y4 Preference of yard 1 with respect to yard 2
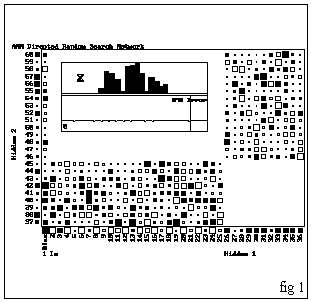
Therefore, the general layout includes 24 neurons in the input layer, 20 and 18 in the hidden layers and 12 in the output layer (see fig.1).